*LONG POST!!, IF DONT WANT TO READ, WATCH THE VIDEO AT THE BOTTOM OF THE PAGE :)*
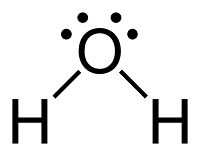
How did we get from this:
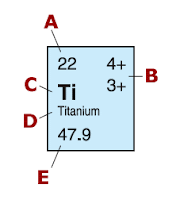
To this:
The very first person to come up with the concept of the atomic theory was Democritus (460 BC - 370 BC). He came up with the thought that everything was made up of matter which was composed of atoms and they looked like tiny spheres. He thought it looked liked this:
Next Aristotle (384 BC - 322 BC) thought up that everything was made up of elements. They were fire, earth, air, water, and aether.
Antoine Lavoisier (Aug.26 1743 - May 8 1794) discovered that water is made of oxygen and hydrogen. He also discovered that chemical elements were neither destroyed or created, but just combined in different compounds in chemical reactions.
John Dalton (Sept. 6 1766 - July. 27 1844) proposed an atomic theory with five major important points. They were 1. Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms, 2. The atoms of a given elements are different from those of any other element, 3. All atoms of a given element are identical, 4. Atoms of one element can combine with atoms of other elements to form chemical compounds, 5. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process.
Henri Becquerel (Dec. 15 1852 - Aug. 25 1908), Marie Curie ( Nov. 7 1867 - July 4 1934) and Pierre Currie (May 15 1859 - Apr. 19 1906) were three physicist who all three won the 1903 Nobel Prize in Physics for their discoveries of radioactivity. In 1911, Marie Currie won the 1911 Nobel Prize in Chemistry for her discovery of the elements Radium and Polonium.
J.J. Thompson (Dec. 18 1856 - Aug. 30 1940) was a physicist who is credited for the discovery of the electron and of isotopes and is the inventor of the mass spectrometer. In 1906, he won the Nobel Prize in Physics for the discovery of the electron and for his work on the conduction of electricity in gases.
Robert Millikan (Mar. 22 1868 - Dec. 19 1953) was an American physicist who discovered the charge on the electron which is negative. He measured the charge with his oil-drop experiment and confirmed that the charges were calculated to be 1.5924(17) x 10^-19.
Ernest Rutherford ( Aug. 30 1871 - Oct. 19 1937) was a New-Zealand born British chemist and physicist who became known as the father of nuclear physics. He discovered the concept of radioactive half life. He directed the Geiger-Marsden experiment in 1909 which proved J.J. Thompson's plum pudding model of the atom was incorrect. His model had the features of a high central charge concentrated in a very small volume in comparison to the rest of the atom and containing the bulk of the atomic mass which would be know as the atomic nucleus. He would also go on to discover the proton in 1919.
Niels Bohr (Oct. 7 1885 - Nov. 18 1962) was a Danish physicist who made contributions of understanding the atomic structure. He created the famous "Bohr Model" which shows the electrons and their orbits around the atom's nucleus.
Henry Moseley (Nov. 23 1887 - Aug. 10 1915) was an English physicist who contributed to concept of the atomic number. He also developed a law called Moseley's Law which also justified many concepts in chemistry by sorting the chemical elements of the Periodic Table of the Elements in a logical order based on physics.
James Chadwick (Oct. 20 1891 - July 24 1974) is known for his discovery of the neutron in 1932. His discovery of the neutron was crucial for the fission of uranium 235. He was later awarded the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1935 for his discovery of the neutron.
NOW FOR A VIDEO!! BONUS: SLIDESHOW OF THE ATOMIC THEORY WITH MILEY CYRUS'S PARTY IN THE USA... just instrumental though :( (Defiantly on the subject of Atomic Theory and Chemistry)TEHE